Docker
Installing and Using Docker with Ubuntu 22.04 (My Personal Machine and Distro)
Resources I am using
Installing Docker
sudo apt update -y
sudo apt install apt-transport-https ca-certificates curl software-properties-common
curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /usr/share/keyrings/docker-archive-keyring.gpg
echo "deb [arch=$(dpkg --print-architecture) signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/docker-archive-keyring.gpg] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu $(lsb_release -cs) stable" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/docker.list > /dev/null
sudo apt update -y
apt-cache policy docker-ce
sudo apt install docker-ceCheck docker status with systemd
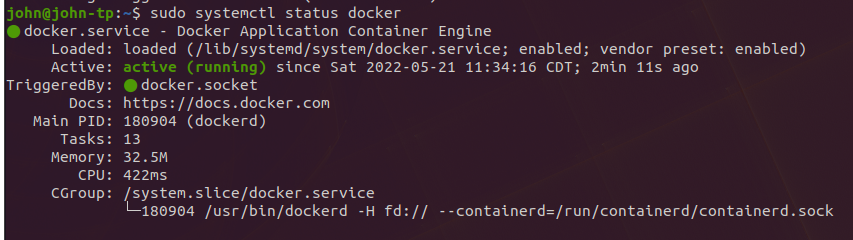
sudo systemctl status dockerView Current Info of Docker Images and Containers
sudo docker infoDocker Images
Docker images can be stored and accessed through Dockerhub. Think of Dockerhub similar to how you would think about Github storing project repositories.
Dockerhub will store images or snapshots of any given project that you can access as long as they are not private in nature.
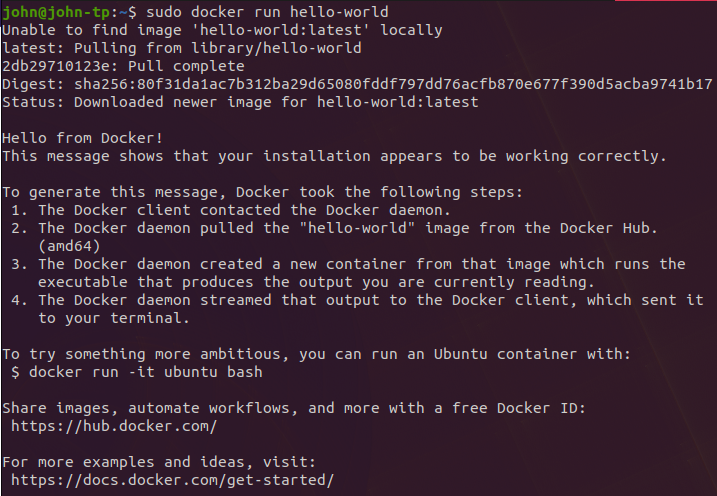
Similar to most tutorials and introductions to new technologies the Digital Ocean walkthrough suggests we attempt to grab a hello-world image from Dockerhub.
In the above example we currently do not have the hello-world image locally on our machine. The docker run command states the following:
docker run: Run a command in a new container. If you do not already have the image it will download and pull the image from dockerhub and finally run the image in a new container on your machine.
docker run hello-worldViewing Downloaded Images
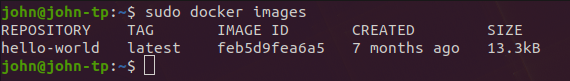
sudo docker imagesOther useful commands
docker ps: view active containersdocker ps -a: view all containers (active or inactive)docker ps -l: view last container createddocker start <container name, id>: start a stopped containerdocker rm: remove a stopped container